SURGICAL MANAGEMENT
Transform Your Life with Expert Weight Loss Surgery
At The Weight Loss Specialist Clinic, we offer advanced weight loss surgery solutions designed to deliver lasting results. If you are considering gastric sleeve, gastric bypass, or revision surgery, we can help. Our experienced surgical team on the Gold Coast is ready to assist you. We offer safe, effective, and personalised care that meets your unique needs.
Why Choose Our Surgical Weight Loss Solutions?
Gastric Sleeve & Gastric Bypass – Proven procedures to support sustainable weight loss and improve health outcomes.
Complete Support Before and After Surgery – From your first meeting to follow-up visits, we help you at every step.
Revisional Surgery & Gastric Band Removal – Expert solutions for patients needing adjustments or corrections to previous weight loss procedures.
One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass (Mini Bypass) – A modern, effective alternative to traditional gastric bypass surgery.
General Surgical Procedures – Including gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy) and hernia repair, to support overall health and wellbeing.
Trusted, Experienced Surgeons – Our top Gold Coast bariatric surgeons focus on minimally invasive weight loss surgery. They ensure the best care possible.
Take Control of Your Health Today
Ready to start your weight loss journey? Book a FREE consultation with our specialists and discover the best surgical solution for you.
Bariatric Surgery: Who Qualifies?
Bariatric surgery is a highly effective long-term weight loss solution for individuals struggling with obesity. According to the International Federation for the Surgery of Obesity & Metabolic Disorders (IFSO) 2022 guidelines, the following criteria determine eligibility for surgery:
BMI Over 35 – Bariatric surgery is recommended for all patients with a Body Mass Index (BMI) over 35.
- Patients with a BMI over 30 can have surgery.
- This applies if they have health issues like diabetes, high blood pressure, or sleep apnoea.
- If your BMI is over 30 and you haven't lost enough weight, you might be eligible for surgery.
- This applies to those who have tried diet, exercise, or medications without success.
Adolescents & Bariatric Surgery – Surgery is suggested for teens with severe obesity. This includes those with a BMI of 120% of the 95th percentile and major health issues. It also applies to those with a BMI of 140% of the 95th percentile. A complete assessment by a team of experts is needed first.
Bariatric Surgery & Other Medical Procedures – Patients with severe obesity may need joint replacement, hernia repair, or organ transplants. They might benefit from bariatric surgery before these procedures.
No Upper Age Limit – There is no strict age limit. However, older adults should have a full health check. This helps to see if they are suitable based on their health and any medical issues.
Weight Loss Surgery Options
Our experienced Gold Coast bariatric surgeon offers a range of advanced weight loss procedures tailored to your individual needs. The most common options include:
Gastric Sleeve (Sleeve Gastrectomy) – Reduces stomach size to help control portion sizes and appetite.
Gastric Bypass (Roux-en-Y Bypass) – Alters digestion to promote weight loss and improve metabolic health.
One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass (Mini Bypass) – A simplified alternative to traditional bypass surgery.
Revisional Bariatric Surgery – Options for patients requiring adjustments or corrections to previous weight loss procedures.
Take the first step towards a healthier future. Book a FREE consultation today to explore the best weight loss surgery option for you.
Surgical options include:
Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy: A Proven Weight Loss Solution
A sleeve gastrectomy is a highly effective weight loss procedure where a thin, vertical portion of the stomach is removed, leaving behind a smaller stomach sleeve. This minimally invasive keyhole surgery reduces stomach capacity and helps control appetite and food intake.
How Does Gastric Sleeve Surgery Work?
A normal stomach can hold up to 2 litres of food. After a sleeve gastrectomy, the stomach capacity is reduced to 100-150ml, significantly limiting food intake.
The portion of the stomach removed is responsible for producing key hunger hormones, leading to reduced appetite, fewer cravings, and improved food choices.
Despite the stomach’s smaller size, digestion remains normal, and the body continues to absorb vitamins and essential nutrients as usual.
Benefits of Sleeve Gastrectomy
Feel Full with Smaller Meals – The restrictive effect of the sleeve allows you to eat less while still feeling satisfied, preventing overeating.
Reduced Hunger & Appetite – Changes in gut hormones result in a natural decrease in hunger, making weight management easier.
Improved Food Preferences – The way the body processes fatty and sugary foods is altered, reducing cravings and promoting healthier eating habits.
Significant Weight Loss – Most patients lose 60-70% of their excess weight, leading to long-term health benefits.
Resolution of Obesity-Related Conditions – Gastric sleeve surgery can result in the rapid resolution of Type 2 diabetes in 80% of patients, often within the first month after surgery—long before major weight loss occurs.
Minimally Invasive & Quick Recovery –
Short hospital stay (1-2 nights).
Less downtime – Most patients return to work within 7 days.
Lower complication risk compared to gastric bypass surgery.
Is Sleeve Gastrectomy Right for You?
If you’re struggling with obesity and non-surgical weight loss methods haven't worked, a gastric sleeve could be the right choice. Our expert Gold Coast bariatric surgeons will assess your health, lifestyle, and goals to determine the best treatment plan for you.
Take the first step towards a healthier, more confident future – Book a consultation today.
Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass: A Gold Standard in Weight Loss Surgery
The gastric bypass is a highly effective and proven weight loss surgery that modifies the digestive system to aid in significant, long-term weight loss. Unlike the gastric sleeve, this procedure alters the pathway of food, creating a small stomach pouch and bypassing the first part of the small intestine.
How Does Gastric Bypass Work?
Smaller Stomach Pouch – Reduces food intake, allowing patients to feel full with smaller portions.
Hormonal Changes – Alters the release of gut hormones, reducing appetite and cravings.
Malabsorption Effect – By bypassing the first section of the small bowel, the body absorbs fewer calories, promoting further weight loss.
Benefits of Gastric Bypass Surgery
Effective for Long-Term Weight Loss – Gastric bypass has a proven track record, remaining the most commonly performed weight loss surgery in the USA for over 20 years.
Resolves Obesity-Related Conditions –
80% of Type 2 Diabetes patients experience remission within weeks of surgery, long before major weight loss occurs.
Significant improvement in high blood pressure, sleep apnoea, and metabolic conditions.
Best Option for Patients with Severe Acid Reflux (GERD) – Unlike the gastric sleeve, the gastric bypass is the preferred surgery for patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and Barrett’s oesophagus.
Minimally Invasive Procedure with Short Recovery –
Hospital stay: 1-2 nights.
Time off work: Typically 5 days.
Is Gastric Bypass Right for You?
If you’re struggling with severe obesity, type 2 diabetes, or chronic acid reflux, gastric bypass surgery may be the best option. Our expert Gold Coast bariatric surgeons will assess your medical history and weight loss goals to recommend the most suitable procedure.
Start your weight loss journey today – book a consultation with our expert team.
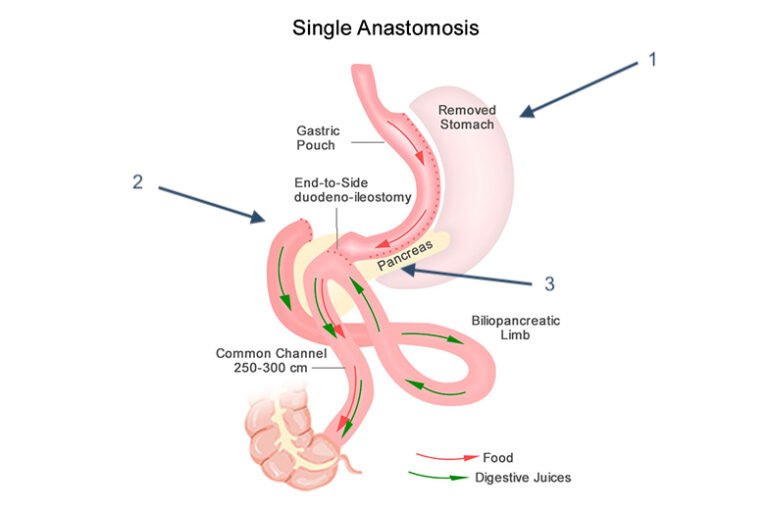
Laparoscopic One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass (Omega Loop) – The ‘Mini Gastric Bypass’
The One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass (OAGB), also known as the Mini Gastric Bypass, is an advanced weight loss surgery that combines restriction and malabsorption for effective, long-term weight loss. This procedure creates a small stomach pouch, which is then connected further down the small intestine, bypassing up to 1.5–2 metres of the digestive tract.
How Does the Mini Gastric Bypass Work?
Smaller Stomach Pouch – Limits food intake, leading to reduced calorie consumption.
Nutrient Absorption Adjustments – Leaves approximately 6 metres of small intestine intact for digestion and absorption.
Single Anastomosis Connection – Unlike the Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass, which involves two connections, the mini bypass has only one, reducing the risk of complications such as bowel herniation.
Benefits of the Mini Gastric Bypass
Less Complex, Shorter Surgery – The procedure typically takes 90 minutes, making it simpler and quicker than the traditional gastric bypass.
Proven Safety & Effectiveness – A minimally invasive laparoscopic procedure with strong weight loss results.
Faster Recovery Time –
Hospital stay: 1-2 nights.
Time off work: Most patients return in 5 days.
Long-Term Weight Loss & Health Benefits –
Effective in resolving obesity-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure.
Alters hunger hormones, reducing appetite and cravings.
Is the Mini Gastric Bypass Right for You?
This less invasive alternative to the Roux-en-Y bypass is ideal for patients looking for a highly effective weight loss procedure with reduced surgical complexity. Our experienced Gold Coast bariatric surgeons will assess your individual needs to determine if this is the best option for you.
Take control of your health – book a FREE consultation today to explore your weight loss surgery options.
Laparoscopic SADI (Single Anastomosis Duodenal-Ileal Bypass with Sleeve Gastrectomy)
The Single Anastomosis Duodenal-Ileal Bypass with Sleeve Gastrectomy (SADI-S) is an advanced weight loss surgery that combines the benefits of a gastric sleeve with an intestinal bypass. This procedure is designed to provide significant, long-term weight loss while reducing the risk of complications associated with traditional bypass surgeries.
How Does the SADI Procedure Work?
Step 1: Sleeve Gastrectomy – The procedure begins with a gastric sleeve, where a portion of the stomach is removed to restrict food intake.
Step 2: Intestinal Bypass – The small intestine is rerouted, bypassing a portion of the digestive tract to limit calorie and nutrient absorption.
Single Connection (Anastomosis) – Unlike the traditional duodenal switch, which requires two connections, SADI has only one, reducing the risk of complications such as bowel obstruction.
Benefits of the SADI-S Procedure
Enhanced Weight Loss & Metabolic Benefits – Patients typically experience greater weight loss than with a standard gastric sleeve or gastric bypass.
Improved Resolution of Obesity-Related Conditions –
80-90% remission rate for type 2 diabetes.
Significant improvements in high blood pressure, sleep apnoea, and metabolic disorders.
Lower Risk of Bowel Complications – Unlike traditional duodenal switch surgery, SADI involves only one surgical connection, reducing the risk of bowel obstruction and internal hernias.
Better Nutrient Absorption Than Traditional Bypass – While some malabsorption occurs, SADI patients typically require fewer vitamin and mineral supplements compared to other bariatric bypass procedures.
Minimally Invasive with Fast Recovery –
Hospital stay: 1-2 nights.
Time off work: Most patients return within 7 days.
Is SADI-S Right for You?
The SADI procedure is an excellent option for individuals with severe obesity, type 2 diabetes, or those seeking greater long-term weight loss than what a gastric sleeve alone can provide. Our Gold Coast bariatric surgeons will assess your health and goals to determine if SADI-S is the best option for you.
Take control of your health – book a FREE consultation today and explore your weight loss surgery options.
The Proven Benefits of Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery is the most effective and long-lasting solution for significant weight loss and obesity-related health improvements. Studies conducted over the last 15 years confirm that surgical weight loss methods outperform non-surgical interventions in terms of safety, effectiveness, and long-term success.
Why Weight Loss Surgery is the Best Option
Clinically Proven Safety & Success – Long-term research confirms the safety, durability, and cost-effectiveness of bariatric procedures.
Low Risk, High Reward – Modern bariatric surgery has a low peri-operative mortality rate of just 0.03–0.2%, making it a safe option for eligible patients.
Resolution of Obesity-Related Conditions – Significant improvements in heart disease, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and metabolic disorders.
Improved Quality of Life – Patients experience increased mobility, energy levels, and overall wellbeing after surgery.
Reduced Long-Term Health Risks – Bariatric surgery leads to a substantial decrease in overall morbidity and mortality, lowering the risk of life-threatening conditions associated with obesity.
Surgical Weight Loss is the Gold Standard
For individuals struggling with severe obesity, bariatric surgery offers a long-term solution with proven health benefits. Our expert Gold Coast weight loss surgeons provide safe, effective, and minimally invasive procedures tailored to your needs.
Take the first step today – book a FREE consultation to explore your weight loss surgery options.